
目前做的项目是android面板和打印机交互App,把交互中用到的机制总结下来供以后参考
交互的基本原理:
打印机通过打印机事件通过广播的方式,通知应用程序,打印机的最新状态。应用程序通过web api 开启打印机扫描、打印以及获取状态信息。
项目需求
应用程序请求扫描/打印任务,把处理扫描/打印任务状态(取消,拒绝,暂停,预览)变为通用逻辑(状态机),把最终结果传递给回调函数
结构图
下面是控制打印机扫描/打印和监听状态的结构图: 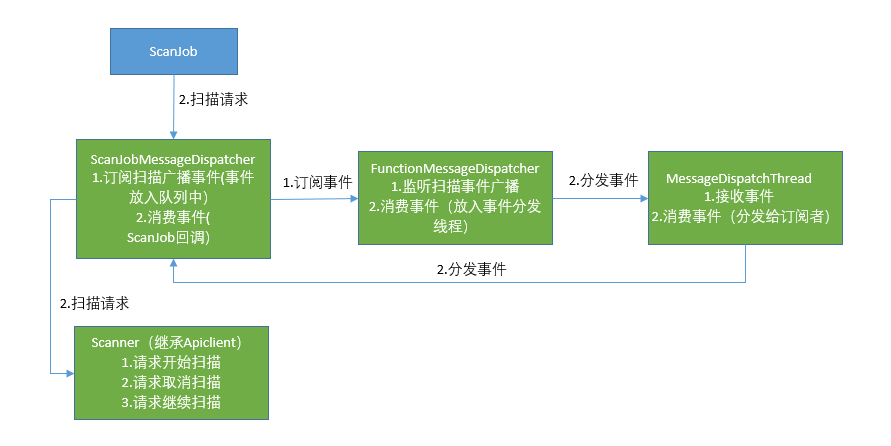
代码分析
Scanjob
从状态机的开始请求开始mApplication.getScanJob().scan(requestAttributes),分析Scanjob类:
public ScanJob(){ this.mHandler = new ScanJobMessageDispatcher(); // sets the listener for the asynchronous communications this.mHandler.setScanJobListener(new JobListener() { @Override public void onChangeJobStatus(ScanJobAttributeSet jobStatus) { changeJobStatus(jobStatus); } @Override public void setJobId(String jobId) { setCurrentJobId(jobId); } @Override public String getJobId() { return getCurrentJobId(); } }); }public boolean scan(ScanRequestAttributeSet attributes) throws ScanException { if( this.mHandler == null ) throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot scan after scanning is completed."); return mHandler.requestStartScanJob(attributes); } 从代码中可以看出:扫描调用的是ScanJobMessageDispatcher的requestStartScanJob方法,ScanJob在构造函数中实例化了ScanJobMessageDispatcher,并且向其注册了监听事件
ScanJobMessageDispatcher
接下来我们看实现requestStartScanJob的ScanJobMessageDispatcher类:
public boolean requestStartScanJob(ScanRequestAttributeSet attributes) throws ScanException { if(this.mJob != null) { throw new ScanException("Can not start scan(), because running scan process."); } // Issues an subscribed ID and registers the asynchronous job event String subscribedId = FunctionMessageDispatcher.getInstance().addAsyncJobEventListener(this); if( subscribedId == null ) { ... } ... Request req = new Request(); ... try { Response resp = mScanner.createJob(req); ... mJob = new Job(jobId); startJobEventDispatcher(jobId); return true; } } catch (IOException e) { ... } catch (InvalidResponseException e) { ... return false; } ... return false; }private void startJobEventDispatcher(String jobId) { finishJobEventDispatcher(); mJobEventDispatcher = new JobEventDispatcher(jobId); mJobEventDispatcher.start(); }@Override public void onReceiveJobEvent(GetJobStatusResponseBody event) { try { mJobEventQueue.put(event); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } }private class JobEventDispatcher extends Thread { private final String mJobId; private volatile boolean mCanceled = false; ... @Override public void run() { Log.d(SmartSDKApplication.getTagName(), PREFIX + "scan job event dispatcher start (" + mJobId + ")"); while (!mCanceled) { GetJobStatusResponseBody event; try { event = mJobEventQueue.take(); ... if (listener != null) { listener.onChangeJobStatus(jobStatusResponseToAttributes(event)); } } catch (InterruptedException ignore) { } } } } 从requestStartScanJob可以看到
1.获取消息接收器的唯一实例,并且向其注册订阅事件,订阅信息是下面的mJob(扫描任务Id)
2.然后通过mScanner调用打印机的web api发起扫描请求
3.最后开始消息读取线程,并将消息传给回调函数。消息处理采用消息队列的目的是: 保证接收到的广播事件串行化处理;不影响消息分发线程的效率
FunctionMessageDispatcher
接下来查看FunctionMessageDispatcher类:
private FunctionMessageDispatcher(){ // Registers an Internal listener to receive asynchronous events from SDKService mScanAsyncEventReceiver = new ScanEventReceiver(); mScanAsyncEventReceiver.addAsyncEventListener(this); mScanner = new Scanner(); }public String addAsyncJobEventListener(AsyncJobEventHandler handler){ if(handler == null) { throw new NullPointerException("handler is null"); } synchronized (mAsyncEvHandlers) { if (mSubscribedId == null) { this.mSubscribedId = mScanAsyncEventReceiver.startReceiveJobEvent(); } if (mSubscribedId != null) { mAsyncEvHandlers.add(handler); } return this.mSubscribedId; } }public String startReceiveJobEvent() { return setReceiveFunctionJobEvent(RECEIVE_SCAN_JOB_STATE_ACTION, true);}String setReceiveFunctionJobEvent(String action, boolean isReceiveEvent){ ... SDKServiceResultReceiver resultReceiver = new SDKServiceResultReceiver(); sendIntent.putExtra("PRODUCT_ID",SmartSDKApplication.getProductId()); ... Handler mHandler = new Handler(this.broadcastResultReceiveThread.getLooper()); SmartSDKApplication.getContext().sendOrderedBroadcast(sendIntent, SDK_SERVICE_SEND_CMD_PERMISSION, resultReceiver, mHandler, Activity.RESULT_OK, null, null); ... // synchronous processing bundle = resultReceiver.getResultExtras(); subscribedId = bundle.getString("SUBSCRIBED_ID"); return subscribedId;}public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { postEvent(EventData.EVENT_TYPE_JOB_EVENT, eventData);}void postEvent(int eventType, String eventData) { this.mMessageThread.post(eventType, eventData, this);}public void onReceiveJobEvent(String eventData) { if(eventData == null) return; Map decoded = GenericJsonDecoder.decodeToMap(eventData); GetJobStatusResponseBody body = new GetJobStatusResponseBody((Map ) decoded.get("data")); String jobId = body.getJobId(); AsyncJobEventHandler[] handlers; synchronized (mAsyncEvHandlers) { handlers = mAsyncEvHandlers.toArray(new AsyncJobEventHandler[mAsyncEvHandlers.size()]); } for(AsyncJobEventHandler handler : handlers) { if( handler.getJobId() == null || handler.getJobId().equals(jobId)) { handler.onReceiveJobEvent(body); } } }MessageDispatchThread.javapublic void run() { while(isStart) { try { EventData ev = mEventQueue.take(); AbstractEventReceiver receiver = ev.getReceiver(); int evType = ev.getEventType(); String data = ev.getEventData(); receiver.notifyAsyncEvent(evType, data); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } } 从addAsyncJobEventListener方法开始
1.startReceiveJobEvent是向系统底层注册扫描事件监听,系统接收到扫描事件后向ScanEventReceiver发送广播
2.把监听器添加到mAsyncEvHandlers注册列表中
3.ScanEventReceiver.onReceive收到事件后把消息分发给线程mMessageThread,MessageDispatchThread.run()消费消息,把消息发送给receiver,receiver就是this.mMessageThread.post(eventType, eventData, this)传入的FunctionMessageDispatcher实例
4.FunctionMessageDispatcher.onReceiveJobEvent把事件发送给所有的订阅者,发送事件的方法是调用ScanJobMessageDispatcher.onReceiveJobEvent把event放入mJobEventQueue队列中。JobEventDispatcher.run读取事件发送给ScanJob的回调函数